Mailgun Node
The Mailgun Node allows a workflow to send emails using the configured Mailgun account.
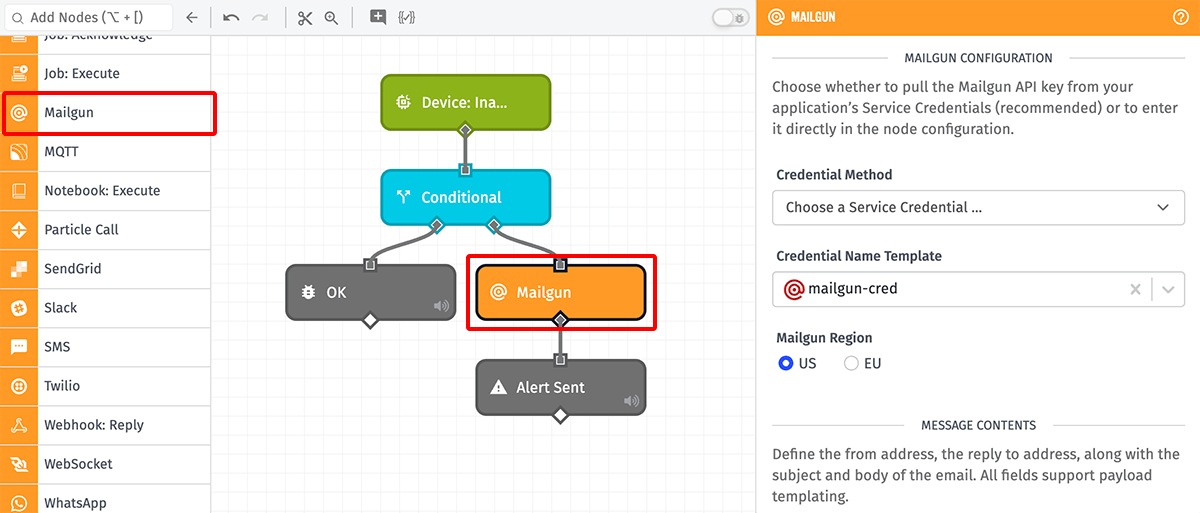
Node Properties
The Mailgun Node takes several configuration properties for authenticating the request, defining the email content, and configuring the recipients ...
Authentication
First, choose whether to authenticate the request from a Mailgun Service Credential (recommended) or to enter your Mailgun API key directly in the node. You may provide either an Account API Key or a Domain Sending Key. We recommend generating a new key specifically for use within this Losant application.
More information on how to create a Mailgun API key can be found in Mailgun's documentation.
Regardless of the chosen authentication method, you must also choose the Region from which to send the message. The default is "US".
Note: Pulling the API key from a service credential is not supported in Edge Workflows.
Message Contents
Next, configure the following fields defining the message contents ...
- From Address Template: A string template for the "From" email address used to deliver the message. To improve the chances of your email being successfully delivered, the domain associated with this address should match a sender domain configured in your Mailgun account.
- Reply-To Template: A string template for the email address where any replies will be sent. This field is optional, and if not provided, replies will be sent to the "From" email address.
- Email Subject Template: A string template for the subject line of the email.
- Email Body Template (HTML): A string template that should resolve to valid HTML, which serves as the message body.
Recipient Addresses
Next, configure the recipients of the email as string templates. At least one "To" address is required; you may also provide one or more "CC" and/or "BCC" addresses.
For each recipient type, addresses may be provided through a combination of the following methods ...
- One address per line.
- Multiple addresses per line, separated by commas (
,) or semicolons (;). - A string template referencing an address, a string of comma- or semicolon-separated addresses, or an array of addresses on the payload.
For example, given the following payload ...
{
"working": {
"emails": [
"success@losant.com, hello@losant.com, support@losant.com",
"administrator@example.com"
],
"extraAddress": "a-third-recipient@example.com"
}
}
... and a Mailgun Node with "To" addresses defined as follows ...
my-recipient@example.com; another-recipient@example.com{{working.extraAddress}}{{working.emails}}
... this would result in emails being sent to seven different addresses.
Attachments
Optionally, you may also add up to 10 attachments to send as part of the email. Each attachment takes the following properties ...
- Input Type: Choose whether to provide the content inline ("File Content Template") or from a URL ("File URL Template"). Depending on the chosen method, you must then provide either ...
- Content Template: A required string template that resolves to some content on your payload in any format (plain text, JSON, binary, etc.). The content will be Base64-encoded for conversion to an attachment, unless the content has already been Base64-encoded.
- URL Template: A required string template that resolves to a publicly available URL from which the attachment can be retrieved. The content will be downloaded from that URL and provided as an attachment on the sent email.
- File Name Template: An optional string template resolving to a file name for the attachment, including the extension. If not provided, default file names will be added.
Result
Optionally, specify a payload path where the result of the send request can be placed on the current payload. This can be used to verify the request was successful or to take another action in the event of an error.
Node Example
If the Mailgun Node successfully sends a message, the following is placed on the payload (assuming a result path of working.mailgunResult) ...
{
"working": {
"mailgunResult": {
"id": "<20240715201459.eccc3cabb22e87b9@sandboxACCOUNT_ID.mailgun.org>",
"message": "Queued. Thank you."
}
}
}
Note: This does not necessarily mean that the email successfully reached all of its recipients - only that the request was successfully sent to Mailgun. The email could have been rejected by the recipient's server or caught by a spam filter. Users should check their Mailgun account logs if messages are not being received as expected.
Node Errors
The Mailgun Node can fail for multiple reasons, and in each case, this will result in an error property being placed on the payload at the provided result path. For example, given a path of working.mailgunResult, the payload would look like the following when trying to use the node with an invalid API key ...
{
"working": {
"mailgunResult": {
"error": "Forbidden"
}
}
}
Another possible error is invalid email addresses being provided for the recipients; in such a case, the Mailgun Node's result may look like the following ...
{
"working": {
"mailgunResult": {
"error": "to parameter is missing"
}
}
}
Related Nodes
Was this page helpful?
Still looking for help? You can also search the Losant Forums or submit your question there.