HTTP Node
The HTTP Node allows a workflow to make an arbitrary HTTP request and optionally place the response on the current payload.
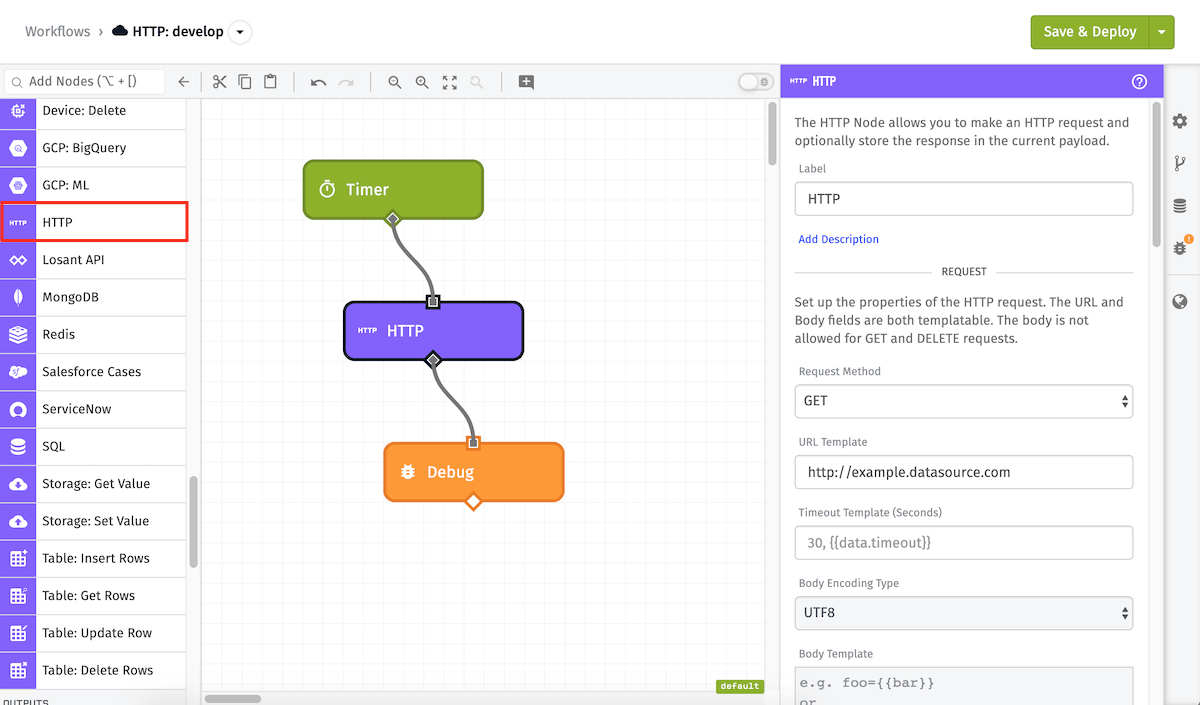
Node Properties
The HTTP Node can be configured with all the common properties of an HTTP request - request method, request URL, request body, and request headers. In addition, the node can optionally store the response of the request at a spot in the payload.
Authorization
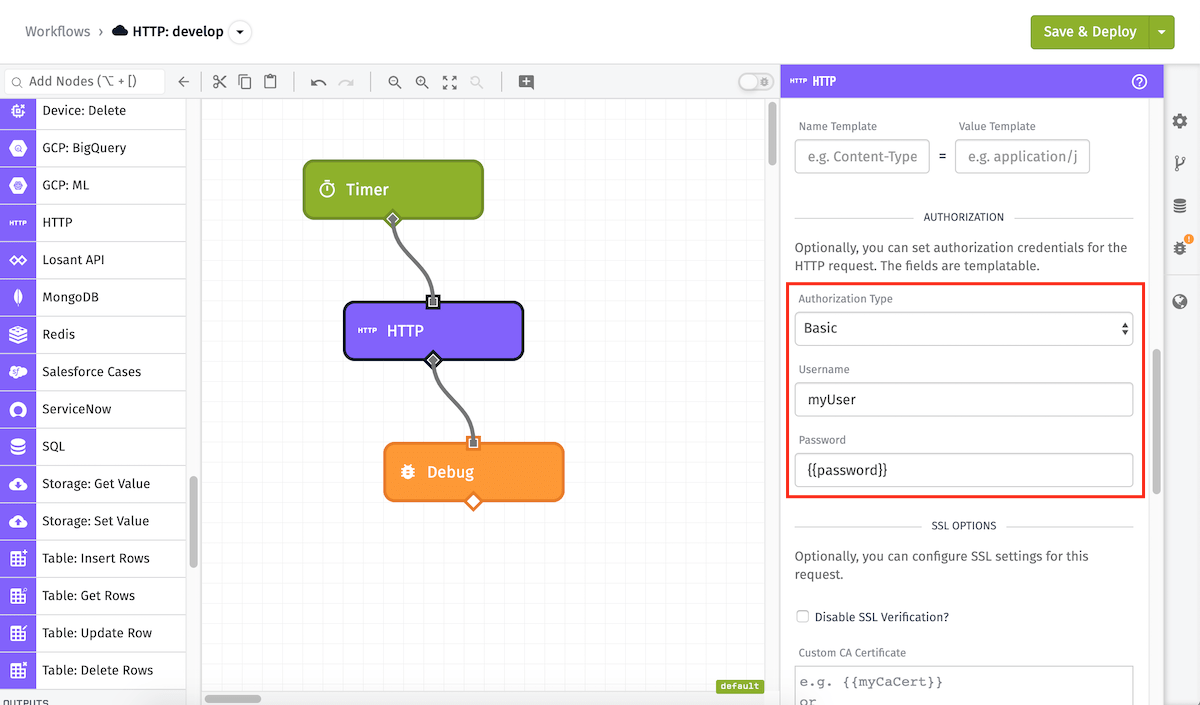
The HTTP Node can optionally set authorization information for requests using the following methods:
- None: No authorization information is sent with the request. Select this option if you are passing authorization info in an HTTP header or as a query parameter on the URL.
- Basic: The request is sent with a Basic authorization header. When selecting this method you can optionally provide a Username and Password, which will automatically be Base64-encoded and sent as part of the "Authorization" header. The screenshot above shows a basic auth configuration, with the username
exampleUserand a string template of{{password}}for the password. For Edge Workflows, the Basic method is only available for workflows targeting GEA version 1.2.0 or higher. For GEA versions before 1.2.0, a username and password can be added to the URI or in the Authorization Header (withusername:passwordBase64-encoded). - Client Certificate: The request is sent with a Client Certificate for the server to authenticate. When selected, you must provide a Client Certificate Key and a Client Certificate. For Edge Workflows, the Client Certificate method is only available for workflows targeting GEA version 1.5.0 or higher.
- Service Credential: The request is sent with the authentication method and URI selected in the Service Credential. Sub-paths and query parameters can be provided to the URI in the URL Template field, and additional headers can be provided so long as they do not conflict with any headers added by the service credential. For Edge Workflows, the Service Credential method is not available.
Request Configuration
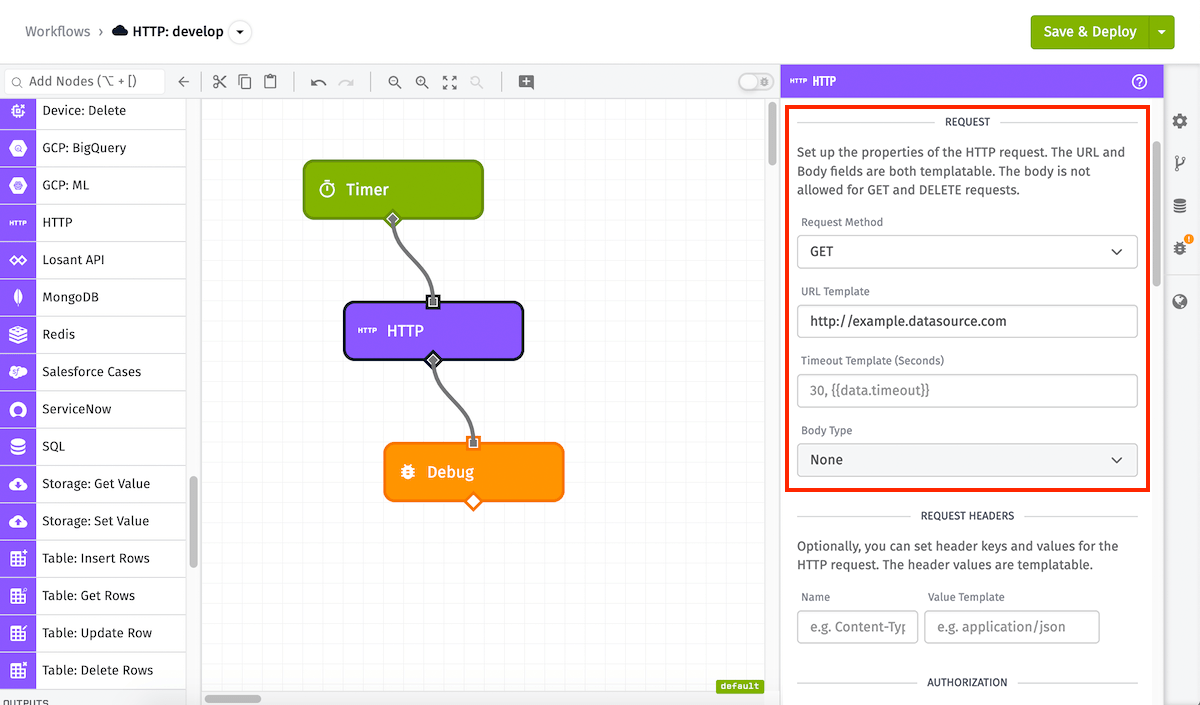
HTTP Request Configuration contains the following fields:
- Request Method (Required): The HTTP request method. Available methods are
GET,POST,PUT,PATCH,DELETE, andHEAD. The method supports string templates. - URL Template (Required): The URL to make the request to. This field supports static URLs or string templates.
- Timeout Template: A string template or integer for the number of seconds to wait before a timeout will occur. The maximum and default timeout is
30. - Body Type: If using a Request Method that allows for sending a body (
POST,PUT,PATCH, andDELETErequests), you must choose a Body Type for constructing the body. Options are:- None: Do not send a body with the request.
- Raw input: This option is selected by default. When choosing this method, you must enter the following fields:
- Body Encoding Type: Select an encoding type for your request body. By default
UTF-8is selected. - Body Template: Enter a value for the body of the request. Many web servers will expect a
Content-Typeheader to be set with a value matching the format of the data submitted here (for example,application/jsonortext/plain).
- Body Encoding Type: Select an encoding type for your request body. By default
- multipart/form-data: Selecting this option submits the body with the multipart/form-data encoding type. Then, enter one or more "Name Template" and "Value Template" values to send as the body.
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded: Selecting this option submits the body with the application/x-www-form-urlencoded encoding type. Then, enter one or more "Name Template" and "Value Template" values to send as the body.
- JSON Template: When selected, Losant will automatically append a
Content-Type: application/jsonheader to the request and will provide a JSON text editor for defining the request body. (Note: If you provide aContent-Typeheader, that header's value will override the automaticapplication/jsonheader.) - URL Template: Selecting this option will make a GET request to the URL you provide and will use the response body as the body of the request for the HTTP Node invocation. This is useful for sending outputs of asynchronous tasks that generate signed URLs - such as notebook executions and data export requests - to third party services.
- Note: When using the option, the request object placed on the payload (if applicable) will contain a
bodyUrlproperty instead of abodyproperty. Its value will be the URL from which the request body was pulled.
- Note: When using the option, the request object placed on the payload (if applicable) will contain a
- Local File Path Template: In edge workflows running GEA version 2.1.0 or higher, you can provide a string template that resolves to a path to a file in the agent's container, the contents of which will serve as the request body.
- Note: When using the option, the request object placed on the payload (if applicable) will contain a
bodyDiskPathproperty instead of abodyproperty. Its value will be the local file path from which the request body was pulled.
- Note: When using the option, the request object placed on the payload (if applicable) will contain a
Header Configuration
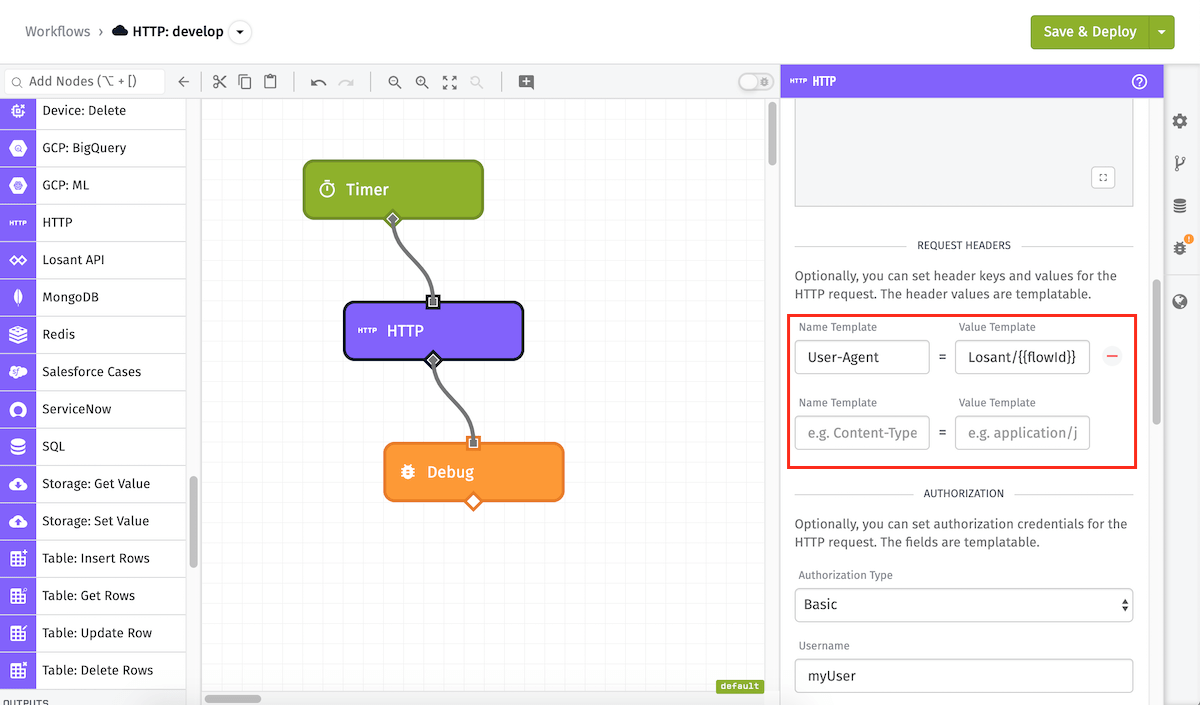
The HTTP Node also has optional support for adding headers to the HTTP request. Each header is a combination of a header name and a header value. Header values can take string templates to dynamically build headers out of the current payload if needed. The above example has a single header of User-Agent whose value is the template Losant/{{flowId}}.
SSL Options
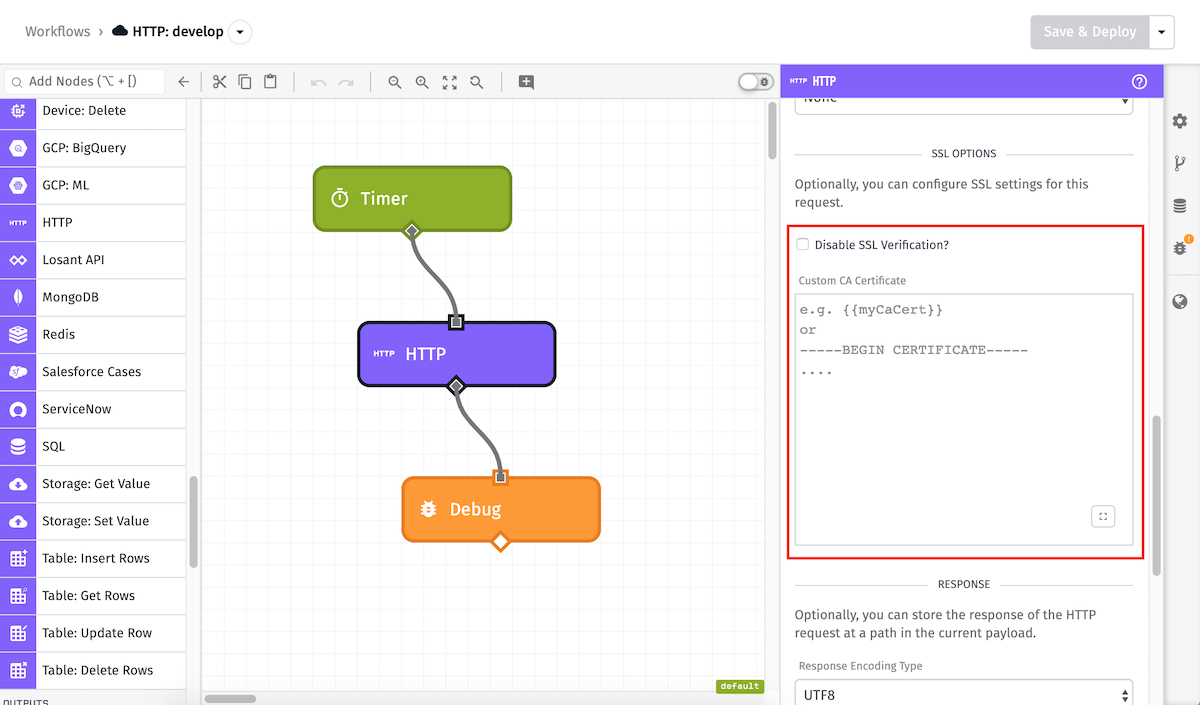
Next, you can decide whether to Disable SSL Verification, which is useful if you are connecting to a server with a self-signed SSL certificate. In the given example, the SSL certificate will still be verified by the request and if it is invalid, the node will return an error. However, if this box was checked, it would not ensure that the SSL certificate is valid.
If you are using a self-signed, custom, or uncommon Certificate Authority, you can also optionally provide the CA certificate. This allows you to keep SSL verification enabled, even when using certificates that Losant normally would not be able to verify.
Response Configuration
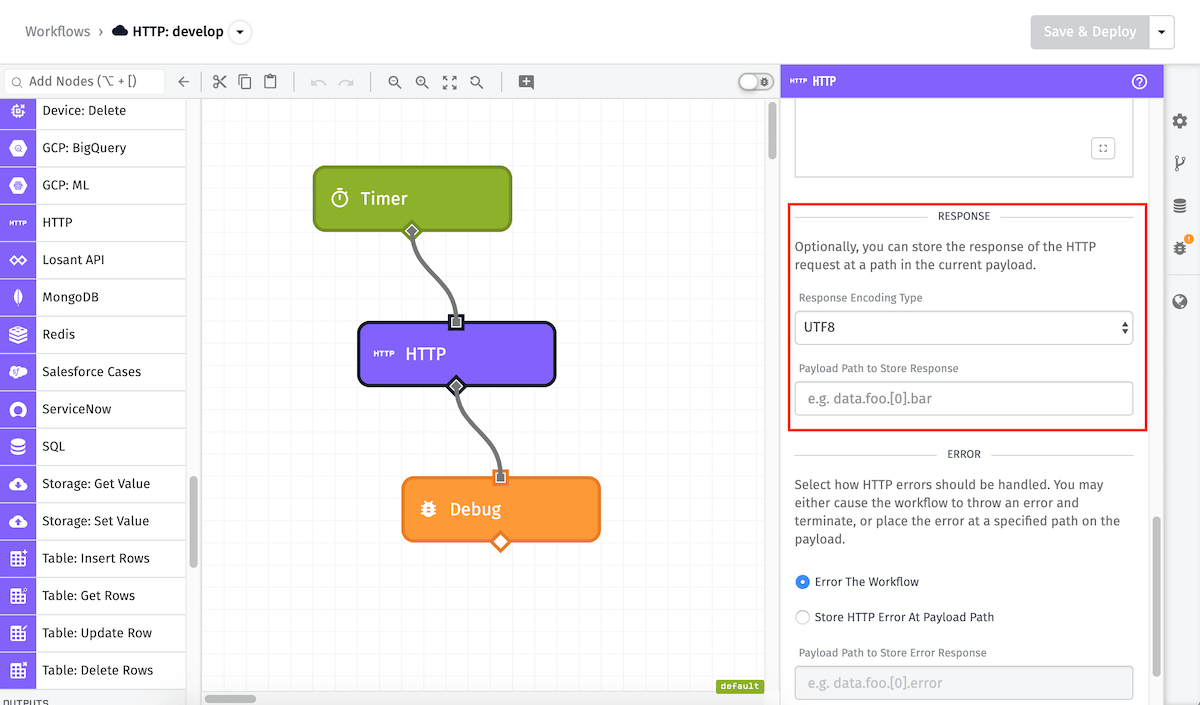
There are two optional fields to set for handling the response to the HTTP request.
- Response Encoding Type: Optionally, you can specify the body response encoding type. By default, the encoding type is
UTF-8. - Local File Path Template: In edge workflows running GEA version 2.1.0 or higher, you may optionally provide a string template that resolves to a file path in the agent's container. If provided, the response body will be written to a file at that path. (This is in addition to the path for storing the response on the payload.)
- Note: When using this option, the payload path for storing the response will contain the local file path at which the response body was stored instead of the response body itself. The other response information (headers, status code, and request duration) as well as the
requestobject will still be placed at the response payload path.
- Note: When using this option, the payload path for storing the response will contain the local file path at which the response body was stored instead of the response body itself. The other response information (headers, status code, and request duration) as well as the
- Payload Path to Store Response: The HTTP Node can optionally store the response from the request at an arbitrary payload path. If a path is defined, the body (or local file path to the body), headers, status code, and original request information are stored at the given path. The node also attempts to parse the body as JSON. If it is parsable, the parsed object is placed on the payload instead of the raw response body string. In the example above, the response will be stored at the
working.resultfield. - Automatically follow redirect responses: If the HTTP Node should automatically follow redirect responses. By default, redirect responses are followed.
Error Configuration
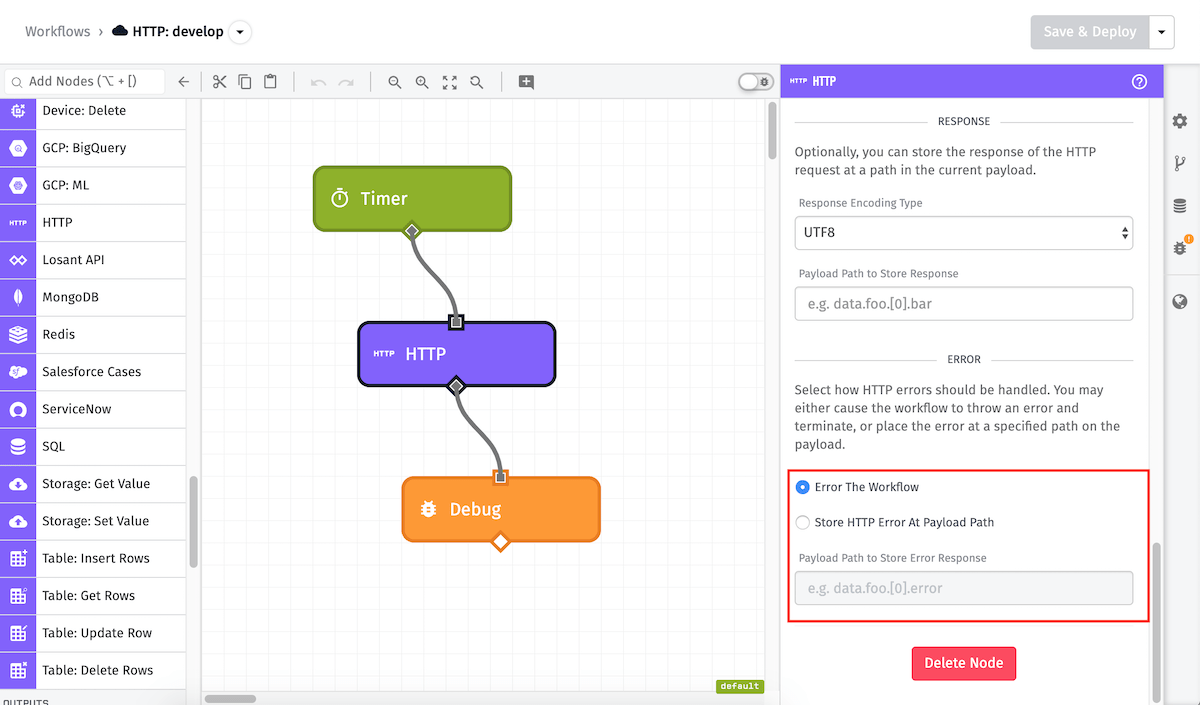
Any HTTP request that returns an actual response (even if it is a 4XX or 5XX status code) will be treated as a response, and so will be stored at the response path. However, there are many reasons why the HTTP node might error without a response, such as timeouts, unreachable servers, DNS resolution failures, and the like.
In those cases, there are two possible options:
- Error The Workflow: The workflow will throw an error, meaning it will stop execution at this node.
- Store HTTP Response At Payload Path: The error can be stored at a path on the payload that you define, in which case the workflow execution will continue. If you choose to store the error at a path on the payload, an object will be placed at that path with the original request information as well as the particular error that occurred.
Edge Workflow Limitations
When using this node in Edge Workflows, some functionality is only available starting with specific GEA versions ...
- The ability to configure error behavior is in GEA version 1.1.1 or higher. In earlier GEA versions, the workflow will throw an error and cease execution if the HTTP Node receives no response.
- The ability to configure SSL Options is in GEA version 1.5.0 or higher.
- The option to set the response encoding type is in GEA version 1.8.0 or higher.
- The option to choose a Body Encoding Type other than
UTF-8is in GEA version 1.9.0 or higher. - The option to select different Body Types is in GEA version 1.30.0 or higher. In previous GEA versions,
Raw inputis the assumed choice, and you must enter a Body Template and a Body Encoding Type. - The
HEADrequest method, and string template support for defining the method, is in GEA version 1.47.0 or higher. - The "From URL" and "JSON Template" Body Type options are in GEA version 1.47.0 or higher.
- The option to configure automatic redirect following is in GEA version 1.50.1 or higher. Prior to this, redirects are always followed.
- The ability to provide a body as part of a
DELETErequest is in GEA version 1.58.0 or higher.
Node Example
With the above example (a GET request to http://example.datasource.com) and the result placed at the payload path of working.httpResponse, a successful response to the request would result in a payload like the following:
- ▶{} 13 keys
- "555555555555eeeeeeeeeeee"
- "My Great Application"
- {} 0 keys
- "333333333333cccccccccccc"
- "My Great Workflow"
- "myFlowVersion"
- ▶{} 3 keys
- "333333333333cccccccccccc-<unique trigger key>"
- "timer"
- Wed Mar 04 2026 01:38:25 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time) (Date object)
- "333333333333cccccccccccc-<unique trigger key>"
- "timer"
- ▶{} 1 key
Node Errors
If Error The Workflow is selected in the Error Configuration, an error object will be placed at the specified payload path (if one is provided. Given an error path of working.httpError and a request the failed due to an invalid URL, an error response would be placed on the payload like so:
- ▶{} 13 keys
- "555555555555eeeeeeeeeeee"
- "My Great Application"
- {} 0 keys
- "333333333333cccccccccccc"
- "My Great Workflow"
- "myFlowVersion"
- ▶{} 3 keys
- "333333333333cccccccccccc-<unique trigger key>"
- "timer"
- Wed Mar 04 2026 01:38:25 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time) (Date object)
- "333333333333cccccccccccc-<unique trigger key>"
- "timer"
- ▶{} 1 key
Limits
The HTTP node has a maximum allowed response body size of 5MB. If the response to a request is larger than 5MB, the node will error with a TooLargeError message. (This limit does not apply when using the Local File Path Template to write the response to a file in edge workflows.)
Related Nodes
Was this page helpful?
Still looking for help? You can also search the Losant Forums or submit your question there.