Azure: Function Node
The Azure: Function Node allows a workflow to execute an Azure Function.
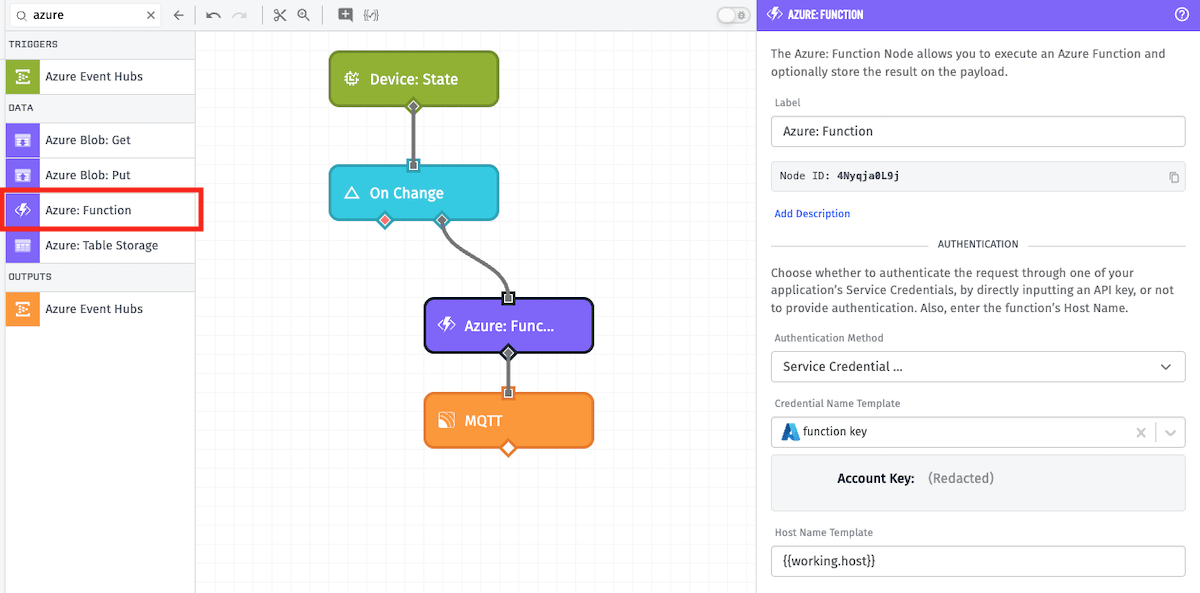
Node Properties
There are several main configuration sections for the Azure: Function Node…
Authentication
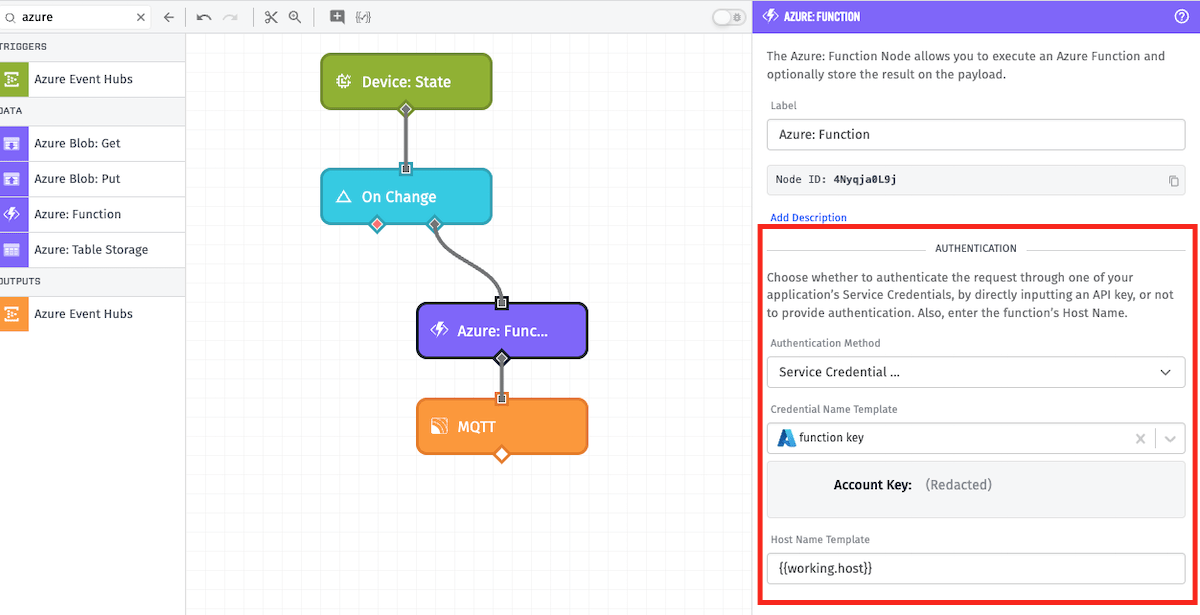
First, enter your Azure credentials.
There are three available Authentication Methods:
- Service Credential: In the
Credential Name Templatefield select an account key previously saved in Losant as an Azure service credential. This field is templatable. Note: This option is not available in Edge Workflows. - API Key: Enter your Azure API key in the
API Key Template. This field is templatable. - No Authentication: Execute the function without authentication.
All authentication methods require Host Name Template - the host name for your Azure Function App. This field is templatable.
Function Configuration
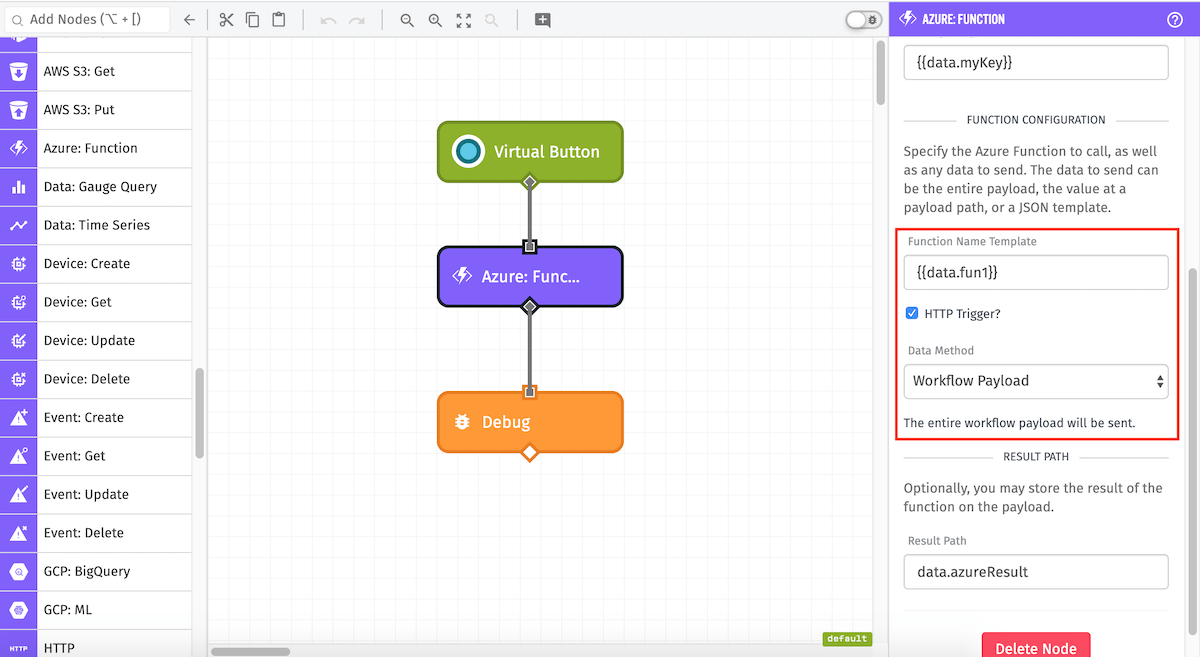
Next, specify the Azure Function to call, as well as any data to send. All applicable fields are templatable.
-
Function Name: (Required) The name of the Azure Function to be called.
- The
HTTP Trigger?checkbox specifies whether the above Azure Function has an HTTP trigger (true) or another one of Azure’s available triggers (false). Defaults to true (checked).
Note: Non-HTTP triggered functions executed in this way must use the master API key.
- The
-
Data Method: The data sent to the Azure Function can be the entire payload, the value at a payload path, or a JSON template.
- Workflow Payload: The entire current payload will be sent to the Azure Function.
- Payload Path: The value at the given payload path will be sent to the Azure Function.
- JSON Template: The value is expected to be a JSON template which will be the object sent to the Azure Function.
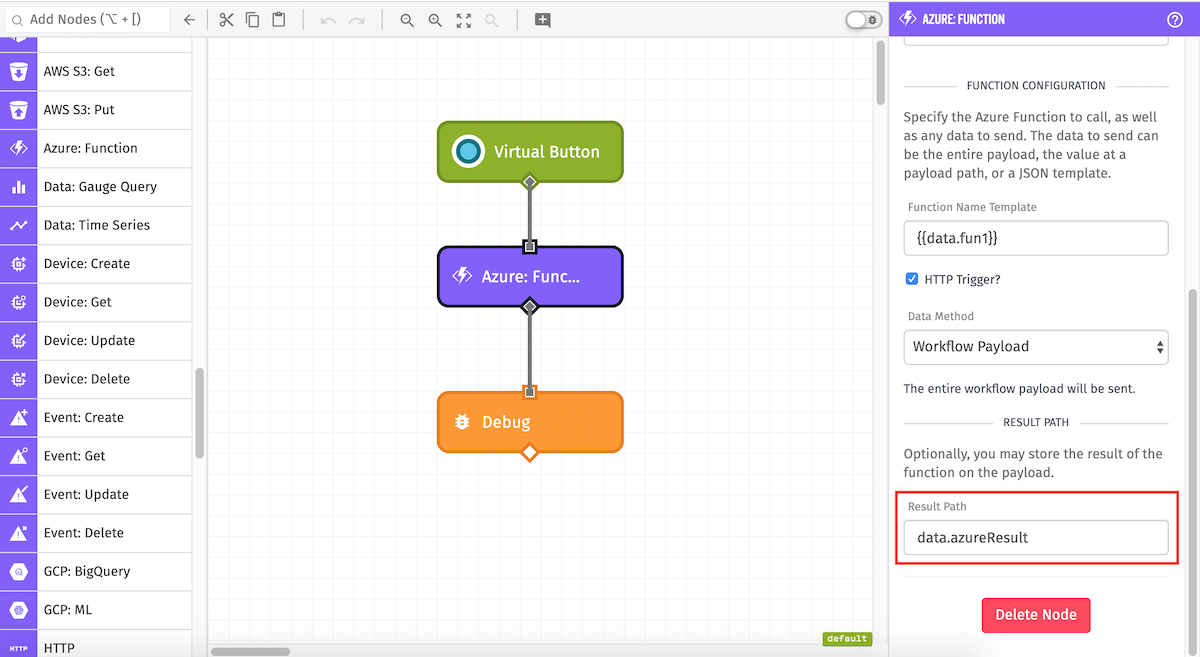
Result Path
Finally, you may optionally store the result of the Azure Function on the payload. More information about returning from Azure Functions can be found in their documentation.
Node Example
If the result path is configured, when a workflow executes an Azure Function its result will be placed on the payload. For example:
Executing the following Azure Function…
module.exports = async function (context, req) {
context.res = {
status: 200,
body: "Hello World!"
}
};results in the following payload:
{
...
"data": {
"azureHeaders": {
"request-context": ...
},
"statusCode": 200
"azureResult": "Hello World!"
}
...
}Node Errors
Errors resulting from configuration of the Azure: Function Node itself will error the workflow like so:
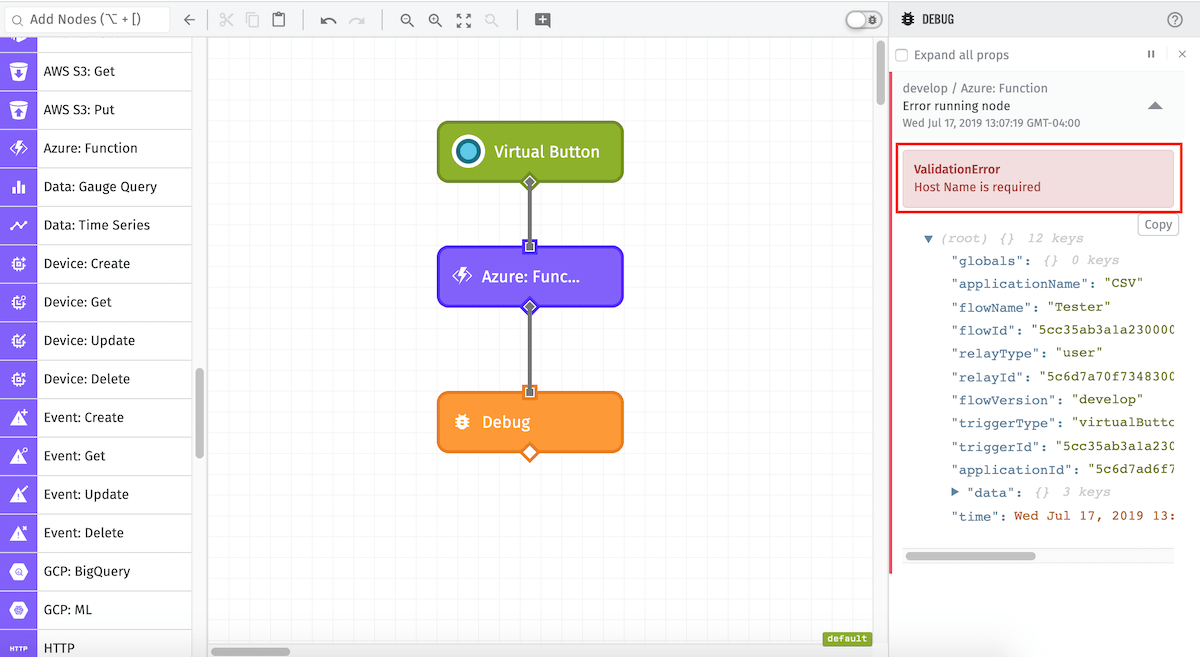
If an error is returned from the Azure Function, it will appear on the payload. Here’s an example of an Azure Function that tried to divide by zero:
{
...
"data": {
"azureResult": {
"ClassName": "System.DivideByZeroException",
"Message": "Attempted to divide by zero.",
"Data": null,
"InnerException": null,
"HelpURL": null,
"StackTraceString": ...,
"RemoteStackTraceString": null,
"RemoteStackIndex": 0,
"ExceptionMethod": null,
"HResult": -2147352558,
"Source": 'f-HttpTrigger1__1168770225',
"WatsonBuckets": null
}
}
...
}Was this page helpful?
Still looking for help? You can also search the Losant Forums or submit your question there.
